www.PimpMyRigAsheville.com434-420-4387 | PimpMyRigAsheville@gmail.com

Pimp My Rig Asheville
Breathe New Life Into Your Older PC or Laptop
or Custom-Build Your Dream
Gaming Rig.
Friendly, Personal Service & High-Quality Work You Can Trust.
Custom PC Upgrades, Re-Builds, New-Builds, and Repairs.
Free pickup & delivery in Asheville, Weaverville, Leicester, Mars Hill, Hendersonville,
Arden, Fletcher, Swannanoa.
Common Computer Terms/Definitions
 BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
Both the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and BIOS are low-level software that starts when you boot your PC before booting your
operating system, but UEFI is a more modern solution, supporting larger hard drives, faster boot times, and more security features.
Both the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and BIOS are low-level software that starts when you boot your PC before booting your
operating system, but UEFI is a more modern solution, supporting larger hard drives, faster boot times, and more security features.
BIOS and UEIF reside on a chip on the machine's motherboard and initializes the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), PCIe (Peripheral Component
Interconnect Express) cards and network devices.
 Bit | Byte | KiloByte | MegaByte | GigaByte | TeraByte
Bit | Byte | KiloByte | MegaByte | GigaByte | TeraByte
A Bit is one unit of memory/storage, which can either be 0 or 1 (off
or on). Eight Bits is called a Byte, which can represent 256
positions/characters. One Kilobyte is 1,024 Bits (~1K Bits or 1
KiloByte). One Megabyte is 1,024 KiloBytes (~1K KiloBytes or 1
MegaByte), and so on.
 Clock Speed (GHz)
Clock Speed (GHz)
The clock speed measures the number of cycles your CPU executes per second, measured in GHz (gigahertz). A CPU with a clock speed of 3.2 GHz executes 3.2 billion cycles per second.
Generally, two CPUs of comparable generation and tier, a higher clock
speed would mean a faster CPU. For example, a 10th generation Intel i7 @
3.6 Ghz would be faster than @ 3.4 GHz; however, an 8th generation Intel
i7 @ 3.2 GHz would be slower than a 10th generation Intel i7 @ 3.2 GHz
 CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of your computer – responsible for carrying out all the instructions that make your computer work.
The CPU is the primary component of any computer or electronic device. It’s responsible for handling the processing of logical and mathematical
operations and executing instructions that it is given. The CPU reads and interprets commands from software programs and uses them to control other
components within the machine. It can execute millions of instructions per second.
 DDR
DDR
Double Data Rate (RAM): A type of computer memory technology that
transfers data between the processor and memory faster than earlier
memory technologies. DDR memory works by transferring data on both the
rising and falling edges of the clock signal, which doubles the data
transfer rate. Each advanced generation of DDR RAM includes a number:
DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, DDR5. DDR supercedes Synchronous Dynamic RAM
(SDRAM). SDRAM waits for clock signals before responding to control
inputs.
Here is a comparison of DDR versions.
 Dual Boot
Dual Boot
Dual booting refers to the process of installing and running two different operating systems on a single computer. This allows you to choose between
the two when you start your computer, giving you the flexibility to switch between them based on your needs. Dual booting allows you to run multiple
operating systems on one machine, which can be beneficial if you need to use specific software that only runs on a particular Operating System (OS).
It also enables you to experiment with different operating systems without having to buy separate hardware. It is possible to dual-boot Windows® and
Linux® on a compatible computer, or dual-boot different versions of Windows®, or different versions of Linux®. To switch between operating systems in a
dual-boot setup, you need to restart your computer and select the desired operating system from the bootloader menu. The bootloader typically appears
during the startup process and allows you to choose between the available operating systems installed on your computer.
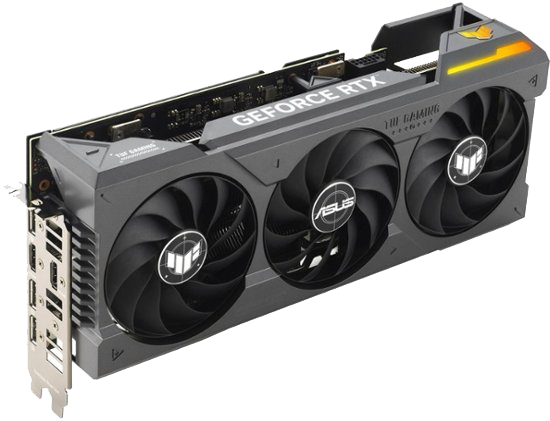 GPU (Graphics Processing Unit/Graphics Card)
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit/Graphics Card)
A GPU (Graphics Processor Unit) is a stand-alone (dedicated) card plugged into the PCI Express (PCIe) bus of a motherboard, or
it can also be part of the motherboard chipset (integrated). It is a programmable processor specialized for rendering all images
on the computer's screen. The more advanced the GPU, the higher the resolution and the faster and smoother the motion. GPUs on
stand-alone cards include their own memory, while GPUs built into the chipset or CPU chip share main memory with the CPU. Major
GPU manufacurers include NVIDA (Geforce), AMD (Radeon), and INTEL (Arc).
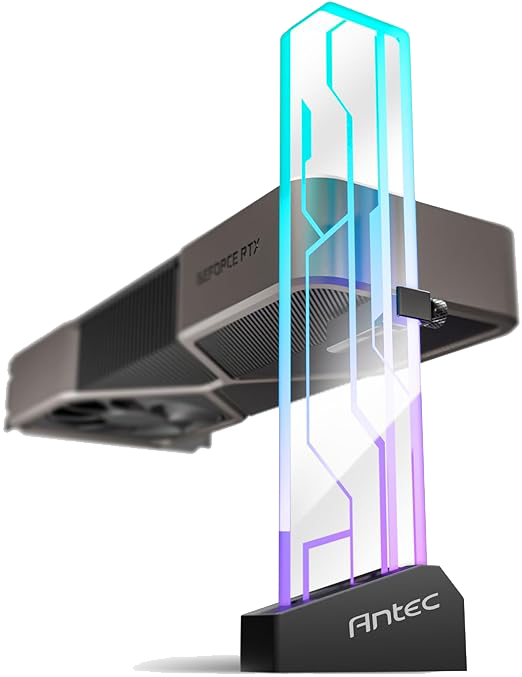 GPU Support Bracket
GPU Support Bracket
A bracket (RGB) that helps support the unfastened end of a GPU inside
the PC case.
 HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse
cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
 Heat Sink/CPU Cooler
Heat Sink/CPU Cooler
A Heatsink/Cooler is used to dissipate heat away from the CPU (Central Processing Unit). The Heatsink acts as a radiator
that conducts heat from the CPU and distributes it through many small metal blades - which is then blown away or cooled by the Heatsink Fan.
Evey CPU requires both a heatsink and fan to keep it operating within a safe temperature range. If a CPU reaches a critically-high unsafe temperature,
it will shut itself down to try and reduce damage caused by overheating.
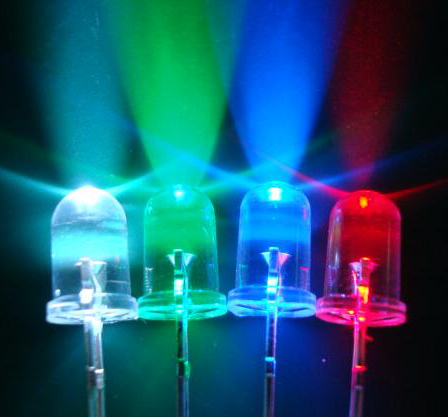 LED
LED
Light-Emitting Dioade - a semiconductor diode that emits light when a voltage is applied to it. LEDs use much less power, last
much longer, and can be smaller than traditional incandescent lights.
 Linux Mint OS
Linux Mint OS
Linux Mint is an Operating System for desktop and laptop computers. It is designed to work 'out of the box' and comes fully equipped with the apps
most people need, including Libre Office, a free complete office
software suite. It is one of the best alternatives to Microsoft Windows and Apple MacOS.
Linux Mint runs great on older CPUs. I've experimented with many Linux
distributions over 10 years and this is my favorite. User-friendly, easy
OS updates, broad printer and hardware support.
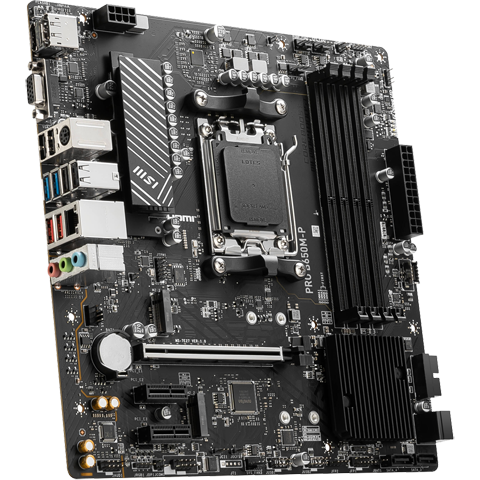 Motherboard (MOBO)
Motherboard (MOBO)
(from TechTarget.com) A motherboard is the main printed circuit board
(PCB) in a computer. The motherboard is a computer's central
communications backbone connectivity point, through which all components
and external peripherals connect. Motherboards can be found in virtually
all computers, especially desktop and laptop PCs. The components that
connect through them include chipsets, central processing units (CPU)
and memory. The external peripherals include Wi-Fi, Ethernet and
graphics cards with the graphics processing unit, or GPU. The PCB of a
large motherboard may include six to 14 layers of fiberglass, copper
connecting traces and copper planes for power and signal isolation.
Other components get added to a motherboard through expansion slots.
These include processor sockets; dual in-line memory modules; Peripheral
Component Interconnect (PCI), PCI Express (PCIe) and solid-state drive
M.2 slots; as well as power supply connections. A heatsink and fan
manage the heat components such as the CPU generate. Typically
motherboards offer additional connectivity through a Southbridge chip
such as PCI, Serial Advanced Technology Attachment or SATA, Thunderbolt,
USB and other interfaces.
The CPU is generally connected to double data rate 3 (DDR3), DDR4, DDR5
or onboard LPDDRx RAM and PCIe. This is done through point-to-point
interconnects such as HyperTransport, Intel's QuickPath Interconnect and
Ultra Path Interconnect. Choosing a motherboard often determines many
features a computer will support. Motherboard designs in desktop
computers typically are the ATX motherboard, which is Intel's improved
version of IBM's AT design. Other form factor designers include the
following: extended ATX, mini-ATX, micro ATX, BTX, micro BTX, mini-ITX,
micro ITX, nano-ITX Some memory controllers are now built into CPUs;
that has eliminated the Northbridge chips that provided memory
management from the motherboard. Integrated video has moved from a
motherboard slotted peripheral to graphics-enabled CPUs. AMD's Ryzen has
a system-on-a-chip design that also makes the Southbridge chipset
optional. This CPU integration has cut motherboard manufacturers' costs.
They can offer base systems for workstations and entry-level computers
and can design customized implementations for various processors that
enable platform upgrades. Gaming motherboards are made for
high-performance computers; they are more powerful and have more
features than motherboards for desktop and laptop computers.
Choosing a Motherboard.
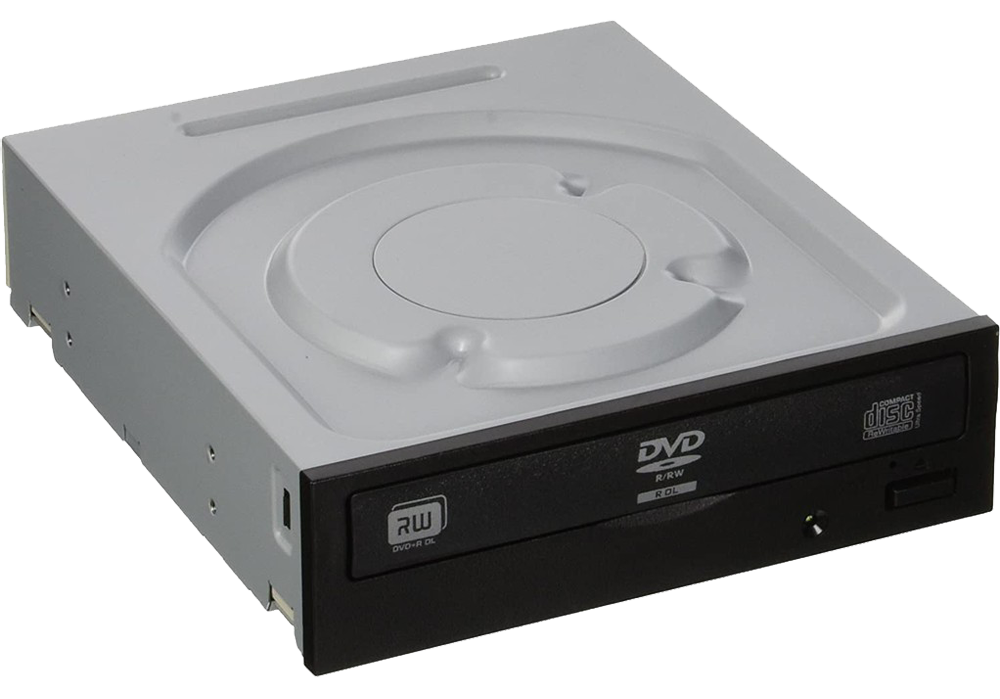 ODD (Optical Disk Drive)
ODD (Optical Disk Drive)
An optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or
electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part
of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some
drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read
and record, also called burners or writers (since they physically burn
the organic dye on write-once CD-R, DVD-R and BD-R LTH discs). Compact
discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which
can be read and recorded by such drives. Although most laptop
manufacturers no longer have optical drives bundled with their products,
external drives are still available for purchase separately, which can
be connected to a computer via USB.
 OS (Operating System)
OS (Operating System)
An operating system (OS) is a program that manages a computer's
hardware and software resources, and provides common services for
computer programs. It's the first program loaded when a computer is
turned on and runs indefinitely until the computer is turned off.
Examples include Microsoft Windows, Apple MacOS, Google Android, and
Linux.
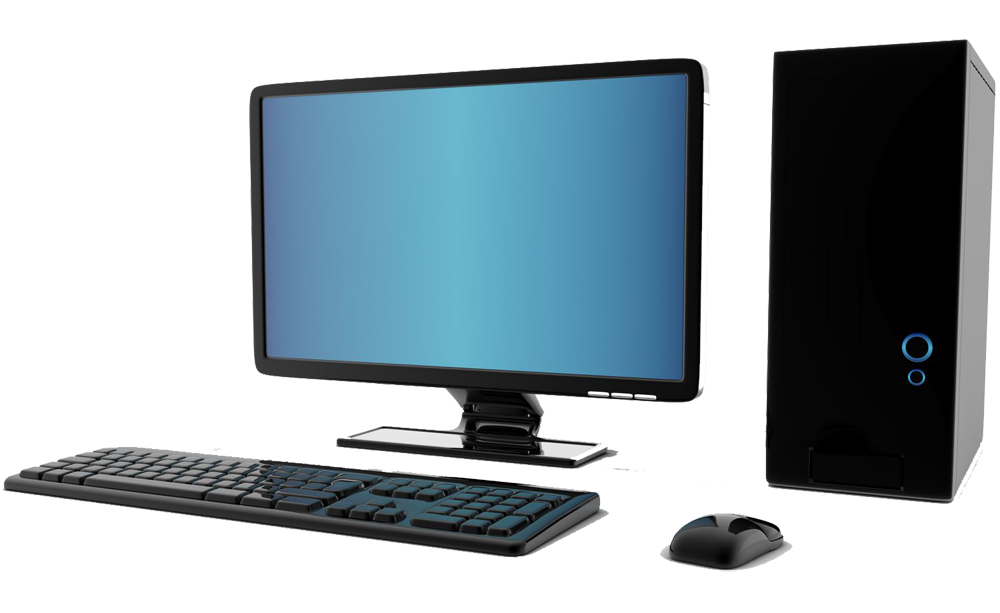 PC (Personal Computer/Desktop Computer)
PC (Personal Computer/Desktop Computer)
PC stands for Personal Computer. Sometimes, PC refers to a Microsoft Windows-based system, as opposed to an Apple-based system: "I'm a Mac, and I'm a PC." Additionally, PC would
differentiate a stationary desktop computer from a laptop or tablet computer.
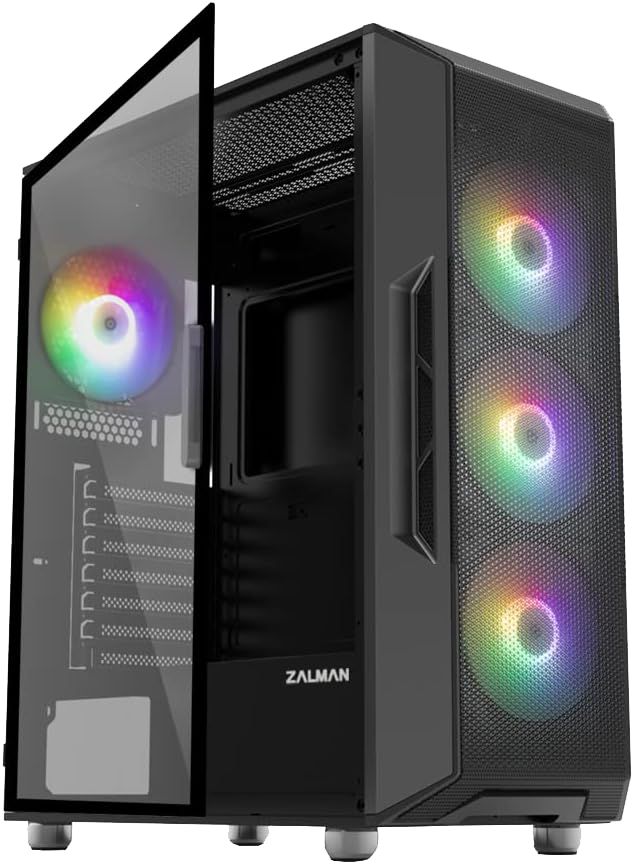 PC Case
PC Case
A PC Case (also called the chassis) can be made of a combination of
metal and plastic, and surrounds and connects all of a computer's
internal components such as the CPU, motherboard, GPU, Power Supply,
etc. A mothernboard size must match the size and form-factor of a PC
Case.
Choosing a PC Case.
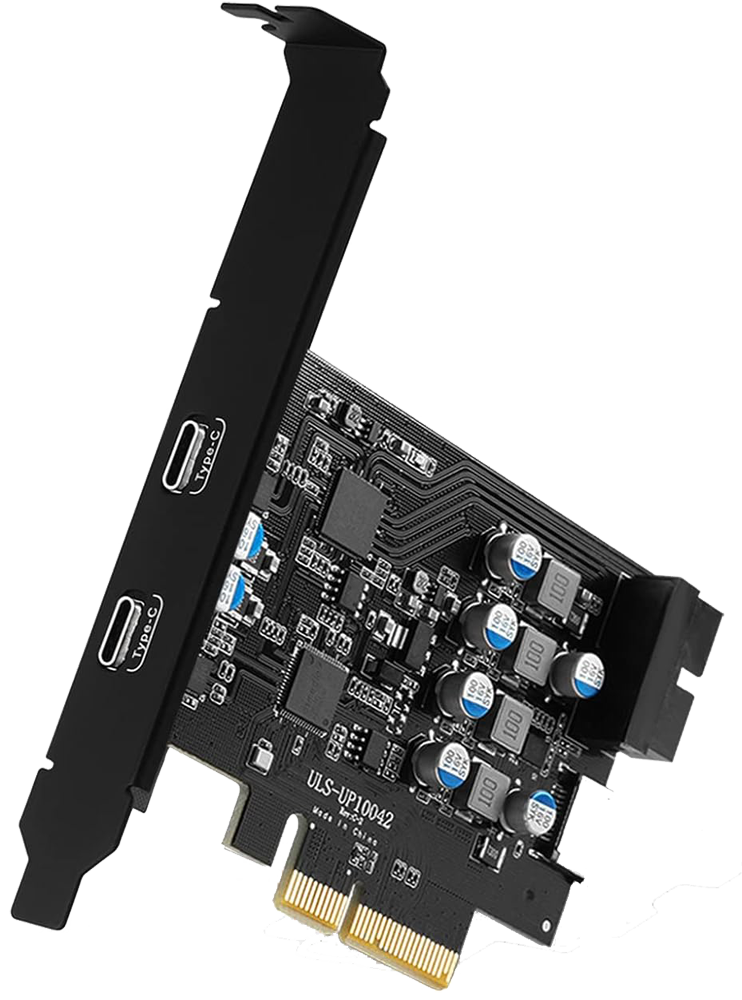 PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)
A high-speed interface standard used for connecting various internal
components in a computer system. PCIe is primarily used for connecting
expansion cards (graphics cards, network cards, storage controllers) to
the motherboard. PCIe slots on a motherboard come in different sizes,
referred to as “lanes”. Common slot configurations include x1, x4, x8,
and x16, which represent the number of data lanes available for
communication. A higher number of lanes generally results in higher data
transfer rates between the motherboard and the expansion card.
 Peripheral
Peripheral
An external device that connects (wired or wireless) to a computer to
expand its capabilities by providing input or output (transferring data
to and/or from). A printer is an output peripheral. A mouse is an input
peripheral.
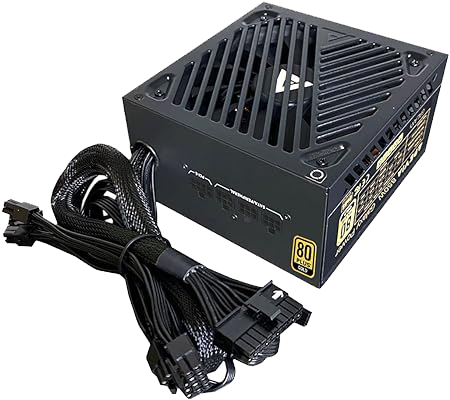 PSU (Power Supply Unit)
PSU (Power Supply Unit)
A PSU converts household AC power to low-voltage regulated DC power
for the internal components of a desktop computer. The wattage of the
PSU must exceed the total power required to power all the internal
coponenents.
 RAM (Random Access Memory/Ready Access Memory)
RAM (Random Access Memory/Ready Access Memory)
RAM is temporary electronic memory that can be read and changed in
any order, used by the CPU to perform calculations.
Here is a comparison of DDR versions.
 RGB (Red, Green, Blue LED Lighting)
RGB (Red, Green, Blue LED Lighting)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse
cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
 SSSD (Solid State Drive)
SSSD (Solid State Drive)
A type of computer storage device that uses flash memory to store
data without moving parts (Solid State = no moving parts). SSDs are a
newer technology that offers several advantages over traditional hard
disk drives (HDDs), including:
Faster read/write speeds, higher reliability, more energy efficient (use
less power, generate less heat), smaller size, less noise.
 UEIF (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
UEIF (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
Both the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and BIOS are low-level software that starts when you boot your PC before booting your
operating system, but UEFI is a more modern solution, supporting larger hard drives, faster boot times, and more security features.
UEIF and BIOS reside on a chip on the machine's motherboard and initializes the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), PCIe (Peripheral Component
Interconnect Express) cards and network devices.
 UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is a device that provides
limited, temporary battery backup power to connected equipment when the
traditional power supply is lost. The UPS plugs into the wall outlet,
and the computer/equipment plugs into the UPS. A UPS will provide enough
time to properly power off computers/electronics and save your work.

© 2023 Pimp My Rig Asheville LLC. All RIghts Reserved.
434-420-4387 | pimpmyrigasheville@gmail.com
Terms & Conditions |
Privacy |
Contact | Logo created by DesignEvo.
Free pickup and delivery in Asheville, Weaverville, Leicester, Mars
Hill, Hendersonville, Arden, Fletcher, Swannanoa.

 BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) Bit | Byte | KiloByte | MegaByte | GigaByte | TeraByte
Bit | Byte | KiloByte | MegaByte | GigaByte | TeraByte  Clock Speed (GHz)
Clock Speed (GHz) CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU (Central Processing Unit) DDR
DDR Dual Boot
Dual Boot GPU (Graphics Processing Unit/Graphics Card)
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit/Graphics Card) GPU Support Bracket
GPU Support Bracket HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) Heat Sink/CPU Cooler
Heat Sink/CPU Cooler LED
LED Linux Mint OS
Linux Mint OS Motherboard (MOBO)
Motherboard (MOBO) ODD (Optical Disk Drive)
ODD (Optical Disk Drive) OS (Operating System)
OS (Operating System) PC (Personal Computer/Desktop Computer)
PC (Personal Computer/Desktop Computer) PC Case
PC Case PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) Peripheral
Peripheral PSU (Power Supply Unit)
PSU (Power Supply Unit) RGB (Red, Green, Blue LED Lighting)
RGB (Red, Green, Blue LED Lighting) SSSD (Solid State Drive)
SSSD (Solid State Drive) UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)